Why DC Switch Disconnectors Are the Safer Choice Over MCBs in DC Power Systems
As solar PV, battery storage, and EV charging continue to expand, the safety of DC power systems has become more critical than ever. While DC MCBs (Miniature Circuit Breakers) are widely used for circuit protection, they are not always the best option—especially when it comes to safe isolation, visibility, and long-term reliability.
This is where DC Switch Disconnectors (DC Isolators) come in. Designed specifically for secure disconnection, they bring an extra layer of protection that MCBs alone cannot provide.
Understanding the Basics
What is a DC MCB?
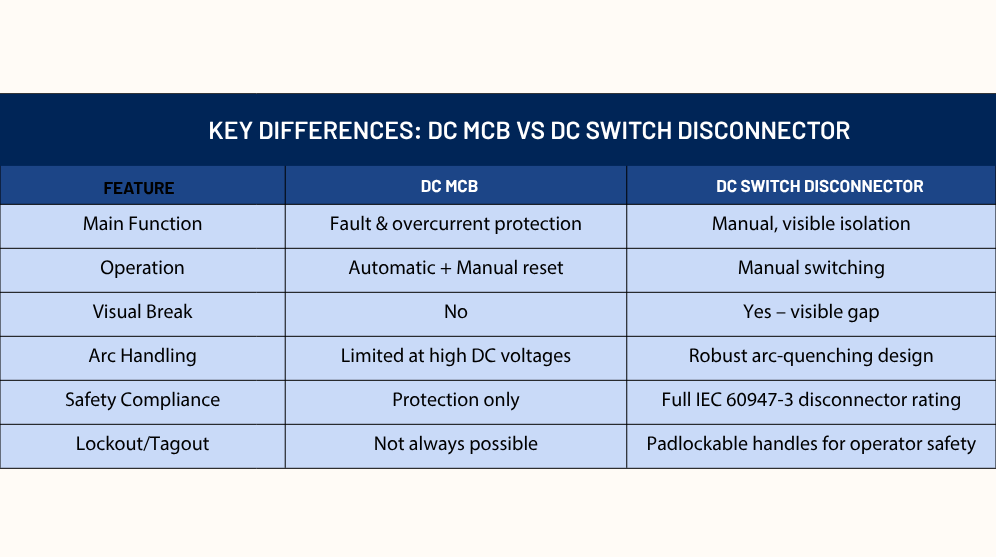
A DC MCB protects circuits against overcurrent and short circuits. It trips automatically when a fault occurs and can be reset manually. However, it is a protection device—not an isolation device
What is a DC Switch Disconnector?
A DC Switch Disconnector is a mechanical device designed for manual, visible isolation of electrical circuits. It ensures a clear, positive break in the circuit, giving operators confidence that the system is fully de-energized and safe to service.
In short:
- MCBs protect circuits.
- Switch Disconnectors isolate them.
Both have their place—but for reliable switching and safe service, disconnectors are indispensable.
Why DC Switch Disconnectors Are Safer than DC MCBs
1. Clear & Visible Isolation
- Switch Disconnector: Provides a visible and positive break of the circuit (I-0 positions clearly indicated). Operators can see and confirm that the circuit is safely isolated before maintenance.
- MCB: Breaks internally; no visible isolation. Even in OFF position, uncertainty may exist about complete disconnection.
2. Knife-Type Contact Advantage
- Switch Disconnector: Uses robust knife-type contacts, creating a wide, visible air gap. This ensures reliable isolation, superior arc suppression, and long-term durability under DC stress.
- MCB: Relies on spring-loaded contacts inside an enclosed mechanism. No visible gap, higher wear, and less confidence in isolation at higher DC voltages.
3. No Risk of Nuisance Trips
- Switch Disconnector: Purely mechanical — isolates only when you decide. Eliminates false trips, which can compromise safety during critical operations.
- MCB: Sensitive to fluctuations, harmonics, or surge events → risk of nuisance tripping → unplanned downtime or even unsafe shutdown.
4. Arc-Safe Operation
- Switch Disconnector: Designed with arc chambers & extinguishing paths suitable for high DC voltages. Operator safety ensured by isolating circuit under controlled conditions.
- MCB: Arc quenching in DC is more difficult (longer arc length vs AC). At higher voltages (like 1000V DC), MCBs struggle, which can lead to unsafe arc propagation.
5. System Safety Compliance
- Switch Disconnector: Complies with IEC 60947-3, specifically tested for isolation, making it a true disconnector (safe for maintenance and service).
- MCB: Complies with IEC 60898/60947-2, primarily a protection device, not validated for isolation.
6. Operator Safety During Maintenance
- Switch Disconnector: Lockable handle options prevent accidental re-energization. Enhances safety for technicians working on panels.
- MCB: Cannot always be lockable; risk of accidental ON during service
7. Designed for Harsh DC Applications
- Switch Disconnector: Built for solar PV, battery storage, and EV systems with high DC voltage and current stresses.
- MCB: Originally designed for AC; adapted to DC but with limitations at higher voltages, making them less safe in demanding DC networks.
Where They Matter Most
- Solar PV arrays
- Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS)
- EV fast-charging infrastructure
- Industrial DC systems
Switch disconnectors are often mandatory at:
- Array combiner boxes
- Inverter DC inputs
- Battery isolators
- Field-level disconnect points
While MCBs protect wiring against faults, they cannot replace the need for a visible, manual isolation point. DC Switch Disconnectors go beyond protection—offering clear disconnection, compliance to IEC 60947-3, and arc-safe design, delivering the safety and peace of mind that MCBs simply cannot match.
FAQs
1. Can a DC Circuit Breaker replace a DC Isolator?
No. A breaker protects against faults but does not provide visible isolation or padlock safety—both essential for maintenance.
2. Why are Switch Disconnectors preferred in DC systems?
Because they combine visible isolation, arc-safe operation, and operator safety measures, making them the preferred choice for modern solar, battery, and EV applications.
Conclusion: Don’t Just Protect—Isolate Safely
In DC systems, protection alone isn’t enough. True safety comes from knowing the system is completely de-energized before work begins.
At Gorlan India, our DC Switch Disconnectors deliver:
- Visible and secure isolation
- Arc-safe, long-lasting performance
- Lockable handles for technician safety
- Rugged operation in harsh environments
👉 For solar, battery, and EV applications, make the safer choice: Switch Disconnectors over MCBs. Because safety is not just about tripping a breaker—it’s about ensuring the power is truly off.
And when it comes to choosing the right disconnector, our F1 Series makes the difference.
IEC/EN 60947-3 compliant and built for rooftop solar and streetlight applications, the F1 handles 32A at 1500V DC and 40A at 1000V DC with ease. With its high insulation strength (Ui = 1500V), rugged outdoor design (Pollution Degree 3, IP66 enclosures), and universal mounting options, it ensures safe and reliable isolation where it matters most.
👉 Discover why professionals trust Gorlan India’s F1 for dependable DC safety.
Related News
Ensuring Zero Downtime with Automatic Transfer Switches of Gorlan India
Gorlan India’s Automatic Transfer Switches enable safe, automatic power transfer to prevent downtime during utility...
Rotary Cam Switches for Generator Panels: Reliable Control and Safety
Rotary cam switches provide reliable control and enhanced safety for generator panels in industrial and...
The Role of Switchgear in the Green Energy Transition
Switchgear plays a critical role in the green energy transition by ensuring safe power switching,...